News from the Institute

Pauline Lascaux, postdoc in the Dikic group, has been awarded a highly competitive MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowship (MSCA PF 2025) for the project „MIND – MINDing the brain“. In her project, Pauline will investigate how the autophagy receptor IRGQ functions as a molecular switch between degradative and secretory autophagy in membrane quality control and neuroinflammation. In particular, she will analyse how IRGQ determines vesicle fate decisions in the brain. By addressing fundamental mechanisms at the intersection of autophagy, membrane biology, and brain inflammation, MIND seeks to generate new insights into the cellular processes that precede neurodegenerative disease.
The MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 call was exceptionally competitive, underscoring the prestige of this award and highlighting the outstanding scientific quality, innovation, and timeliness of the funded project. Out of 17,066 applications submitted, only1,610 proposals were selected for funding by the European Commission.

Alexandra Stolz, has been featured in the Journal of Cell Science’s ‘Cell Scientists to Watch’ series. In the interview, Alexandra talks openly about what sparked her fascination with cell biology, the people and moments that shaped her scientific path, and the excitement and challenges of starting her own lab. She also reflects on leadership, resilience in academia, and how curiosity and persistence guide her work both in and beyond the lab.
Cell Scientists to Watch is a long-standing editorial series that highlights early independent cell biologists whose work has attracted attention within the international research community.

In their latest work, a team of researchers led by Ivan Dikic shows that the DPC-repair enzyme SPRTN works not only during DNA replication but also in mitosis to clear these DNA lesions. When SPRTN is impaired, damaged DNA leaks into the cell’s cytoplasm and activates the cGAS-STING innate immune pathway, leading to chronic inflammation.
... (read more)
IBC2 Director Ivan Đikić will be awarded the prestigious Theodor Bücher Medal from the Federation of European Biochemical Societies (FEBS) in recognition of his outstanding achievements in biochemistry and molecular biology.
... (read more)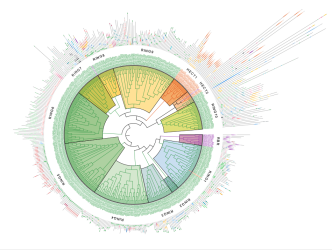
In a new publication in Nature Communications, a team of researchers from IBC2 at Goethe University Frankfurt, reports the first comprehensive, data-driven classification of all human E3 ubiquitin ligases. The study presents a systematic map of the human “E3 ligome” and provides new insights into the functional relationships among E3 ligases.
... (read more)