News from the Institute

This was the slogan of a public TEDx event in Zagreb, at which IBC2 director Ivan Dikic shared his thoughts about what can be learnt from bacteria. It was the largest Croatian TED event ever, full of enthusiasm, creativity and inspiration.
The 20 speakers came from many different areas of society, and all gave one major motivation message: boundaries can be broken if we just strive hard enough.
... (read more)
A team around Ivan Dikic and Mike Heilemann (Chemistry Department, Goethe University) gained unprecedented insight into the mechanism by which cells fight Salmonella infections. Upon intracellular invasion, bacteria are usually rapidly surrounded by a coat of ubiquitin, the function of which remained unclear until now.
Combining super-resolution microscopy with cell biological analysis, the researchers now discovered that distinct ubiquitin chains transform the bacterial surface into a molecular signalling platform. They were able to visualize the nanoscale distribution of different ubiquitin chains on the bacterial surface.
... (read more)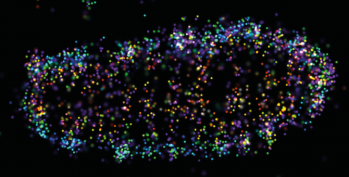
IBC2 director Ivan Dikic has been awarded with an Advanced Investigator Grant of the European Research Council (ERC). It is the second time that Dikic receives the prestigious grant which entails funding in the amount of € 2.5 million for the next five years.
Within his new project, Dikic is investigating how bacteria manipulate the ubiquitin system of their host organism. "Bacteria are rapidly changing chemical factories that subdue human cells and exploit them for their own needs. We focus on foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli and Shigella that cause around 200 million infections and more than 250.000 deaths per year”, explains Dikic. “We will investigate how bacterial toxins containing different enzymatic activities cause cell and tissue damages, eventually resulting in symptoms of infection.”

Timurs Maculins, postdoctoral scientist in the group of Ivan Dikic at IBC2, was awarded a 2-year postdoctoral fellowship by the AXA Research Fund. The funded project will focus on how pathogenic bacteria hijack the host cell and suppress its immune response, ultimately aiming at finding new antibiotics.
The AXA Research Fund grants 25 postdoctoral fellowships annually for postdoctoral researchers and is dedicated to boosting scientific discoveries that contribute to societal progress. It was established in 2007 and has since then supported more than 500 research projects, hosted in 34 countries, aiming to foster research on risks and challenges today’s societies are faced by.
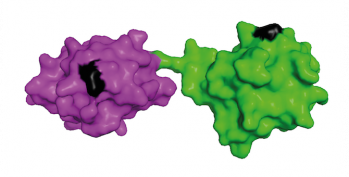
Ubiquitin molecules can be attached to each other to build longer chains with unique 3D structures mediating diverse functions. About a decade ago, linear ubiquitin chains, in which the head of one ubiquitin is linked to the tail of another, were identified as a new chain type involved in inflammatory signalling.
However, target proteins of linear ubiquitination and their specific functions have largely remained elusive. A novel technology developed by an international team around IBC2 group leader Koraljka Husnjak now enables the systematic analysis of linear ubiquitination targets. Details are published in today’s online issue of Nature Methods.
... (read more)